C++的22种设计模式 | Word count: 7.5k | Reading time: 41min
C++的22种的设计模式,分析其使用的设计思想
参考源码地址
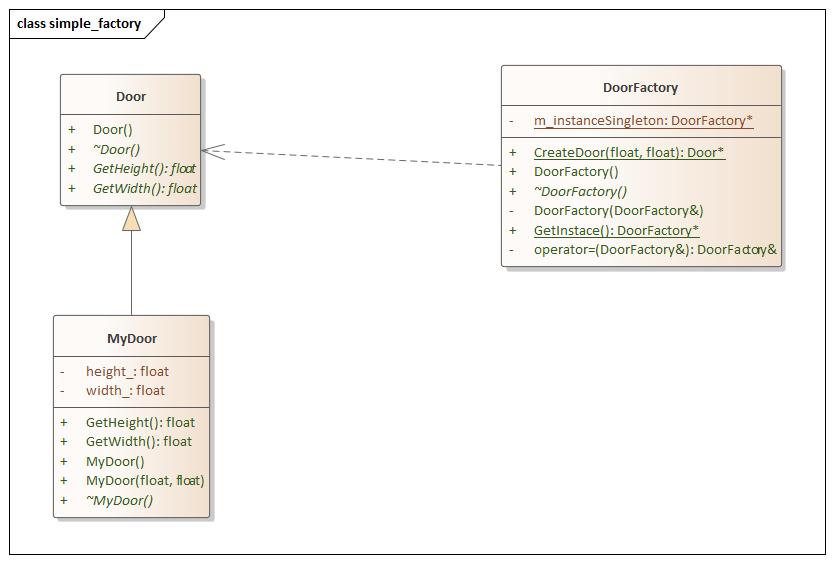
创建型 SimpleFactory(简单工厂) 设计思想
Code
simple_factory.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #ifndef PRODUCT_H #define PRODUCT_H #include <iostream> namespace simple_factory {class Door { public : Door () = default ; virtual ~Door () = default ; virtual float GetHeight () 0 ; virtual float GetWidth () 0 ; }; class MyDoor :public Door { public : using Door::Door; MyDoor () = default ; MyDoor (float height, float width) : height_ (height), width_ (width) { } virtual ~MyDoor () = default ; float GetHeight () override return height_; } float GetWidth () override return width_; } private : float height_; float width_; }; class DoorFactory { public : DoorFactory () = default ; virtual ~DoorFactory () = default ; static DoorFactory* GetInstace () return m_instanceSingleton; } static Door* CreateDoor (float height, float width) return new MyDoor (height, width); } private : DoorFactory (const DoorFactory&) = delete ; DoorFactory& operator =(const DoorFactory&) = delete ; static DoorFactory* m_instanceSingleton; }; DoorFactory* DoorFactory::m_instanceSingleton = new DoorFactory; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <iostream> #include "simple_factory.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace simple_factory;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) DoorFactory *door_factory = DoorFactory::GetInstace (); float height = 1.7 ; float width = 2.1 ; Door* my_door = door_factory->CreateDoor (height, width); cout << "Height: " << my_door->GetHeight () << endl; cout << "Width: " << my_door->GetWidth () << endl; return 0 ; }
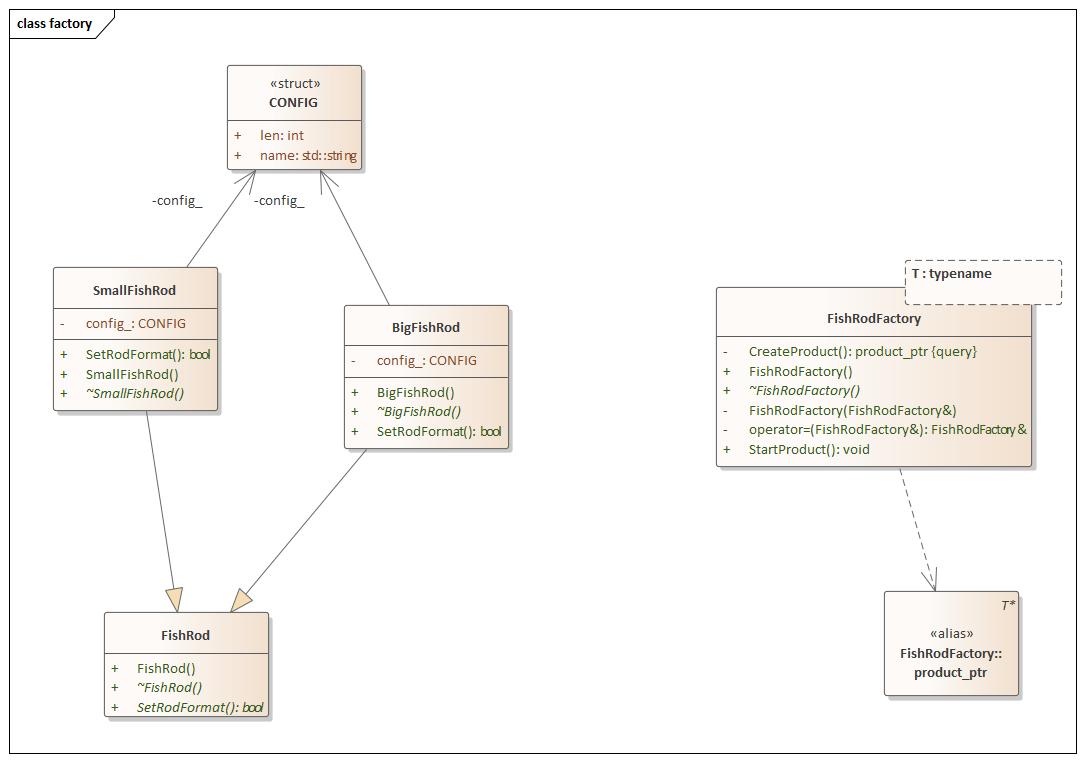
Factory(工厂方法) 设计思想
Code
factory.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 #ifndef FACTORY_H #define FACTORY_H #include <iostream> namespace factory {using namespace std;typedef struct { std::string name; int len; } CONFIG; class FishRod { public : FishRod () = default ; virtual ~FishRod () = default ; virtual bool SetRodFormat () 0 ; }; class SmallFishRod :public FishRod{ public : SmallFishRod () = default ; virtual ~SmallFishRod () = default ; using FishRod::FishRod; bool SetRodFormat () override cout << "Small Fish Rod" << endl; } private : CONFIG config_; }; class BigFishRod :public FishRod{ public : BigFishRod () = default ; virtual ~BigFishRod () = default ; bool SetRodFormat () override cout << "Big Fish Rod" << endl; } private : CONFIG config_; }; template <typename T>class FishRodFactory { using product_ptr = T*; public : FishRodFactory () = default ; virtual ~FishRodFactory () = default ; void StartProduct () auto fish_rod = this ->CreateProduct (); fish_rod->SetRodFormat (); } private : product_ptr CreateProduct () const { return new T (); } FishRodFactory (const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; FishRodFactory& operator =(const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; }; template class FishRodFactory <template class FishRodFactory <#if 0 class FishRodFactory { public : FishRodFactory () = default ; virtual ~FishRodFactory () = default ; void StartProduct () FishRod *fish_rod = this ->CreateProduct (); fish_rod->SetRodFormat (); } virtual FishRod* CreateProduct () 0 ; private : FishRodFactory (const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; FishRodFactory& operator =(const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; }; template <typename T>class OtherFishRodFactory :public FishRodFactory{ public : OtherFishRodFactory () = default ; virtual ~OtherFishRodFactory () = default ; FishRod* CreateProduct () override { return new T (); } private : OtherFishRodFactory (const OtherFishRodFactory&) = delete ; OtherFishRodFactory& operator =(const OtherFishRodFactory&) = delete ; }; #endif } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <iostream> #include "factory.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace factory;extern template class FishRodFactory <extern template class FishRodFactory <int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) FishRodFactory<BigFishRod> big_fish_rod; FishRodFactory<SmallFishRod> small_fish_rod; big_fish_rod.StartProduct (); small_fish_rod.StartProduct (); #if 0 FishRodFactory *big_fish_rod = new OtherFishRodFactory<BigFishRod>(); FishRodFactory *small_fish_rod = new OtherFishRodFactory<SmallFishRod>(); big_fish_rod->StartProduct (); small_fish_rod->StartProduct (); #endif return 0 ; }
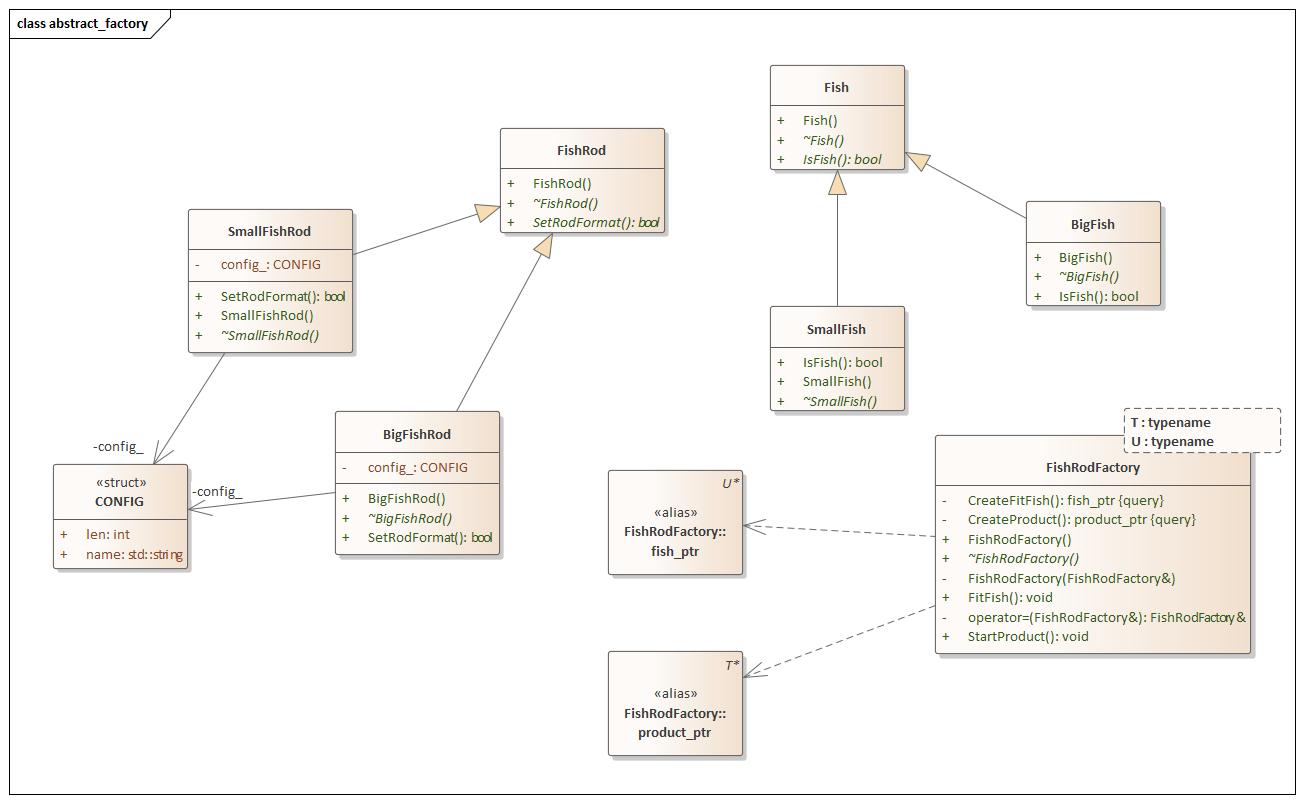
AbstractFactory(抽象工厂) 设计思想
Code
abstract_factory.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 #ifndef ABSTRACT_FACTORY_H #define ABSTRACT_FACTORY_H #include <iostream> namespace abstract_factory {using namespace std;typedef struct { std::string name; int len; } CONFIG; class FishRod { public : FishRod () = default ; virtual ~FishRod () = default ; virtual bool SetRodFormat () 0 ; }; class SmallFishRod :public FishRod{ public : SmallFishRod () = default ; virtual ~SmallFishRod () = default ; using FishRod::FishRod; bool SetRodFormat () override cout << "Small Fish Rod" << endl; } private : CONFIG config_; }; class BigFishRod :public FishRod{ public : BigFishRod () = default ; virtual ~BigFishRod () = default ; bool SetRodFormat () override cout << "Big Fish Rod" << endl; } private : CONFIG config_; }; class Fish { public : Fish () = default ; virtual ~Fish () = default ; virtual bool IsFish () 0 ; }; class BigFish :public Fish{ using Fish::Fish; public : BigFish () = default ; virtual ~BigFish () = default ; bool IsFish () override cout << "Is Big Fish" << endl; } }; class SmallFish :public Fish{ using Fish::Fish; public : SmallFish () = default ; virtual ~SmallFish () = default ; bool IsFish () override cout << "Is Small Fish" << endl; } }; template <typename T, typename U>class FishRodFactory { using product_ptr = T*; using fish_ptr = U*; public : FishRodFactory () = default ; virtual ~FishRodFactory () = default ; void StartProduct () auto fish_rod = this ->CreateProduct (); fish_rod->SetRodFormat (); } void FitFish () auto fit_fish = this ->CreateFitFish (); fit_fish->IsFish (); } private : product_ptr CreateProduct () const { return new T (); } fish_ptr CreateFitFish () const { return new U (); } FishRodFactory (const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; FishRodFactory& operator =(const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; }; template class FishRodFactory <template class FishRodFactory <#if 0 class FishRodFactory { public : FishRodFactory () = default ; virtual ~FishRodFactory () = default ; virtual FishRod* CreateProduct () 0 ; virtual Fish* CreateFitFish () 0 ; private : FishRodFactory (const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; FishRodFactory& operator =(const FishRodFactory&) = delete ; }; template <typename T, typename U>class OtherFishRodFactory :public FishRodFactory{ public : OtherFishRodFactory () = default ; virtual ~OtherFishRodFactory () = default ; FishRod* CreateProduct () override { return new T (); } Fish* CreateFitFish () override { return new U (); } private : OtherFishRodFactory (const OtherFishRodFactory&) = delete ; OtherFishRodFactory& operator =(const OtherFishRodFactory&) = delete ; }; #endif } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> #include "abstract_factory.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace abstract_factory;extern template class FishRodFactory <extern template class FishRodFactory <int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) FishRodFactory<BigFishRod, BigFish> big_fish_rod; FishRodFactory<SmallFishRod, SmallFish> small_fish_rod; big_fish_rod.StartProduct (); big_fish_rod.FitFish (); small_fish_rod.StartProduct (); small_fish_rod.FitFish (); #if 0 FishRodFactory *big_fish_rod_factory = new OtherFishRodFactory<BigFishRod, BigFish>(); { FishRod *big_fish_rod = big_fish_rod_factory->CreateProduct (); big_fish_rod->SetRodFormat (); Fish *big_fish = big_fish_rod_factory->CreateFitFish (); big_fish->IsFish (); } FishRodFactory *small_fish_rod_factory = new OtherFishRodFactory<SmallFishRod, SmallFish>(); { FishRod *small_fish_rod = small_fish_rod_factory->CreateProduct (); small_fish_rod->SetRodFormat (); Fish *small_fish = small_fish_rod_factory->CreateFitFish (); small_fish->IsFish (); } #endif return 0 ; }
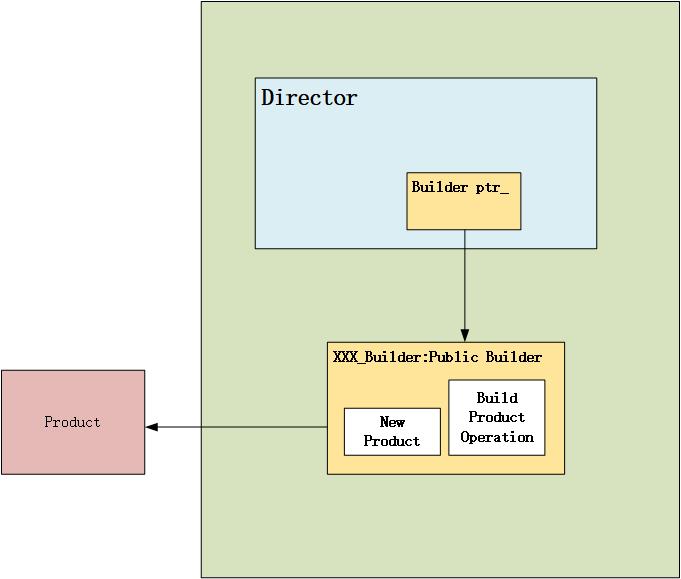
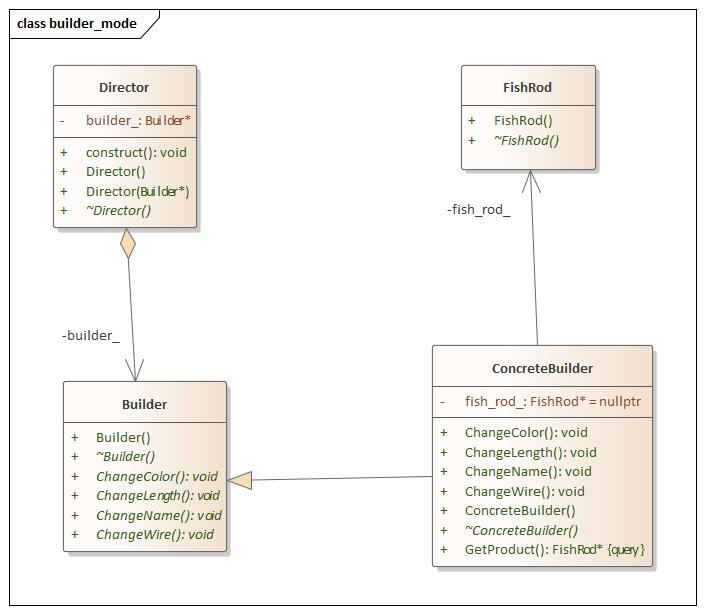
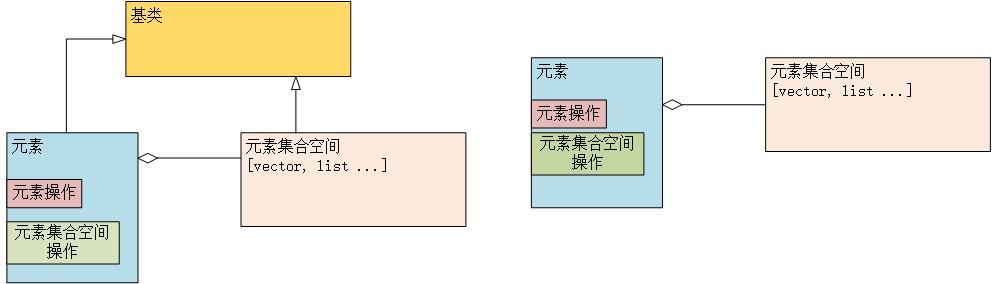
Builder(生成器) 设计思想 new出一个Product,调用创造这个产品的方法,将最终的Product通过接口返回。
Code
builder.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #ifndef BUILDER_H #define BUILDER_H #include <iostream> namespace builder_mode {class FishRod { public : FishRod () = default ; virtual ~FishRod () = default ; }; class Builder { public : Builder () = default ; virtual ~Builder () = default ; virtual void ChangeWire () 0 ; virtual void ChangeColor () 0 ; virtual void ChangeLength () 0 ; virtual void ChangeName () 0 ; }; class ConcreteBuilder :public Builder{ using Builder::Builder; public : ConcreteBuilder () = default ; virtual ~ConcreteBuilder () = default ; void ChangeWire () override std::cout << "Change Wire" << std::endl; } void ChangeColor () override std::cout << "Change Color" << std::endl; } void ChangeLength () override std::cout << "Change Length" << std::endl; } void ChangeName () override std::cout << "Change Name" << std::endl; } FishRod* GetProduct () const { return new FishRod; } private : FishRod *fish_rod_ = nullptr ; }; class Director { public : Director () = default ; Director (Builder* p_builder) { builder_ = p_builder; } virtual ~Director () = default ; void construct () builder_->ChangeColor (); builder_->ChangeName (); builder_->ChangeWire (); builder_->ChangeLength (); } private : Builder *builder_; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <iostream> #include "builder.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace builder_mode;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Director *b = new Director (new ConcreteBuilder); b->construct (); return 0 ; }
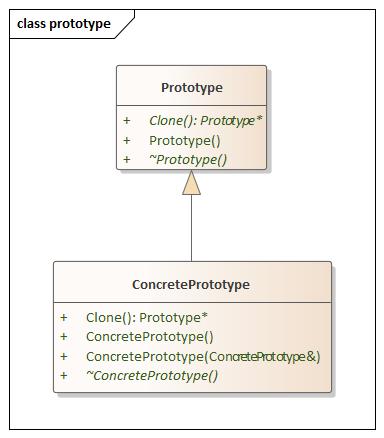
Prototype(原型) 设计思想
Code
prototype.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #ifndef PROTOTYPE_H #define PROTOTYPE_H namespace prototype {class Prototype {public : Prototype () = default ; virtual ~Prototype () = default ; virtual Prototype* Clone () 0 ; }; class ConcretePrototype :public Prototype{ using Prototype::Prototype; public : ConcretePrototype () = default ; ConcretePrototype (const ConcretePrototype&) = default ; virtual ~ConcretePrototype () = default ; Prototype* Clone () override { return new ConcretePrototype (*this ); } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <iostream> #include "prototype.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace prototype;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Prototype *p = new ConcretePrototype; Prototype *q = p->Clone (); return 0 ; }
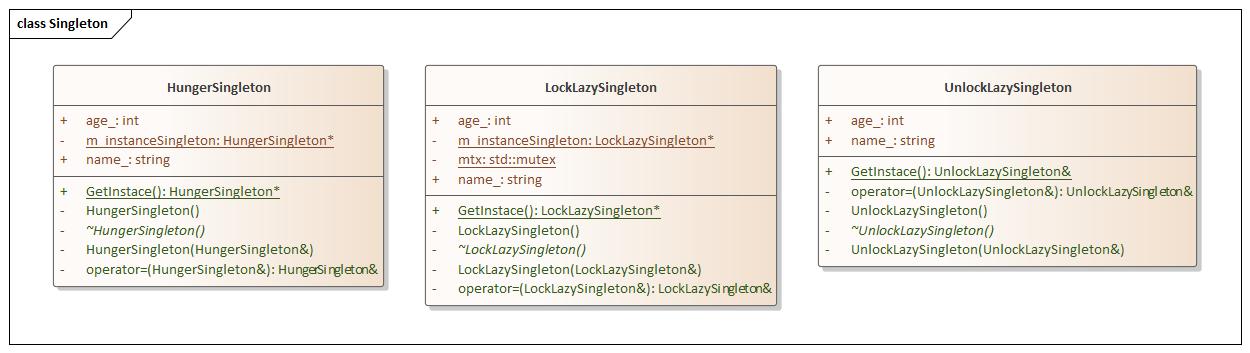
Singleton(单例) 单例就是Cpp中设计的全局变量,通过禁止拷贝函数和赋值操作,保证整个工程只有一个类,通过静态函数和静态变量的特殊性,静止生成新的对象。设计思想
两种模式
Code
饿汉模式
hunger_singleton.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #ifndef HUNGER_SINGLETON_H #define HUNGER_SINGLETON_H #include <iostream> using namespace std;class HungerSingleton { public : static HungerSingleton* GetInstace () string name_; int age_; private : HungerSingleton (); virtual ~HungerSingleton (); HungerSingleton (const HungerSingleton&); HungerSingleton& operator =(const HungerSingleton&); static HungerSingleton *m_instanceSingleton; }; HungerSingleton* HungerSingleton::m_instanceSingleton = new HungerSingleton; HungerSingleton::HungerSingleton () { } HungerSingleton::~HungerSingleton () { } HungerSingleton* HungerSingleton::GetInstace () return m_instanceSingleton; } #endif
加锁懒汉模式
lock_lazy_singleton.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #ifndef LOCK_LAZY_SINGLETON_H #define LOCK_LAZY_SINGLETON_H #include <iostream> #include <mutex> using namespace std;class LockLazySingleton { public : static LockLazySingleton* GetInstace () string name_; int age_; private : LockLazySingleton (); virtual ~LockLazySingleton (); LockLazySingleton (const LockLazySingleton&); LockLazySingleton& operator =(const LockLazySingleton&); static LockLazySingleton *m_instanceSingleton; static std::mutex mtx; }; LockLazySingleton* LockLazySingleton::m_instanceSingleton = nullptr ; std::mutex LockLazySingleton::mtx; LockLazySingleton::LockLazySingleton () { std::cout << "Create LockLazySingleton" << std::endl; } LockLazySingleton::~LockLazySingleton () { } LockLazySingleton* LockLazySingleton::GetInstace () if (m_instanceSingleton == NULL ) { mtx.lock (); if (m_instanceSingleton == NULL ) { m_instanceSingleton = new LockLazySingleton; } mtx.unlock (); } return m_instanceSingleton; } #endif
Main调用
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 #include <iostream> #include "lock_lazy_singleton.h" #include "unlock_lazy_singleton.h" #include "hunger_singleton.h" using namespace std;void ShowLockLazySingleton () LockLazySingleton *lock_lazy_singleton = LockLazySingleton::GetInstace (); cout << lock_lazy_singleton->name_ << endl; cout << lock_lazy_singleton->age_ << endl; } void ShowUnLockLazySingleton () cout << UnlockLazySingleton::GetInstace ().name_ << endl; cout << UnlockLazySingleton::GetInstace ().age_ << endl; } void ShowHungerSingleton () HungerSingleton* hunger_singleton = HungerSingleton::GetInstace (); cout << hunger_singleton->name_ << endl; cout << hunger_singleton->age_ << endl; } int main () LockLazySingleton *lock_lazy_singleton = LockLazySingleton::GetInstace (); lock_lazy_singleton->name_ = "xiao ming" ; lock_lazy_singleton->age_ = 24 ; UnlockLazySingleton::GetInstace ().name_ = "xiao hong" ; UnlockLazySingleton::GetInstace ().age_ = 22 ; HungerSingleton* hunger_singleton = HungerSingleton::GetInstace (); hunger_singleton->name_ = "xiao gang" ; hunger_singleton->age_ = 23 ; ShowLockLazySingleton (); ShowUnLockLazySingleton (); ShowHungerSingleton (); hunger_singleton->name_ = "xiao hua" ; hunger_singleton->age_ = 25 ; ShowHungerSingleton (); return 0 ; }
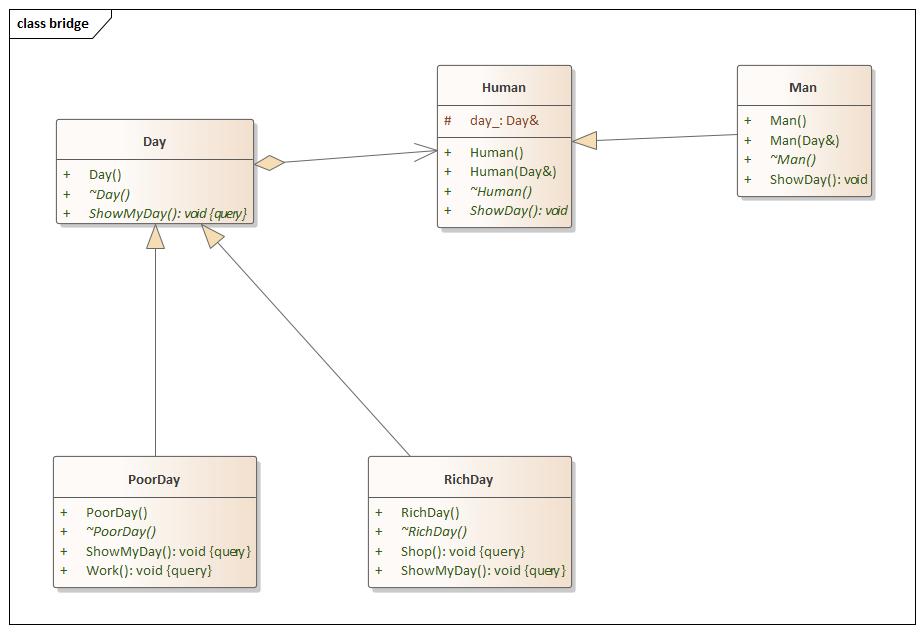
结构型 Bridge(桥接) 设计思想
Code
bridge.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #ifndef BRIDGE_HPP #define BRIDGE_HPP #include <iostream> namespace bridge {class Day {public : Day () = default ; virtual ~Day () = default ; virtual void ShowMyDay () const 0 ; }; class PoorDay :public Day{public : PoorDay () = default ; virtual ~PoorDay () = default ; void ShowMyDay () const override Work (); } void Work () const std::cout << "I Need To Work." << std::endl; } }; class RichDay :public Day{public : RichDay () = default ; virtual ~RichDay () = default ; void ShowMyDay () const override Shop (); } void Shop () const std::cout << "I Will To Shop" << std::endl; } }; class Human {public : Human () = default ; Human (Day& day) : day_ (day) {} virtual ~Human () = default ; virtual void ShowDay () 0 ; protected : Day& day_; }; class Man :public Human {public : Man () = default ; Man (Day &day) : Human (day) {} virtual ~Man () = default ; void ShowDay () override day_.ShowMyDay (); } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <iostream> #include "bridge.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace bridge;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) PoorDay poor_day; Man poor_man (poor_day) ; poor_man.ShowDay (); RichDay rich_day; Man rich_man (rich_day) ; rich_man.ShowDay (); return 0 ; }
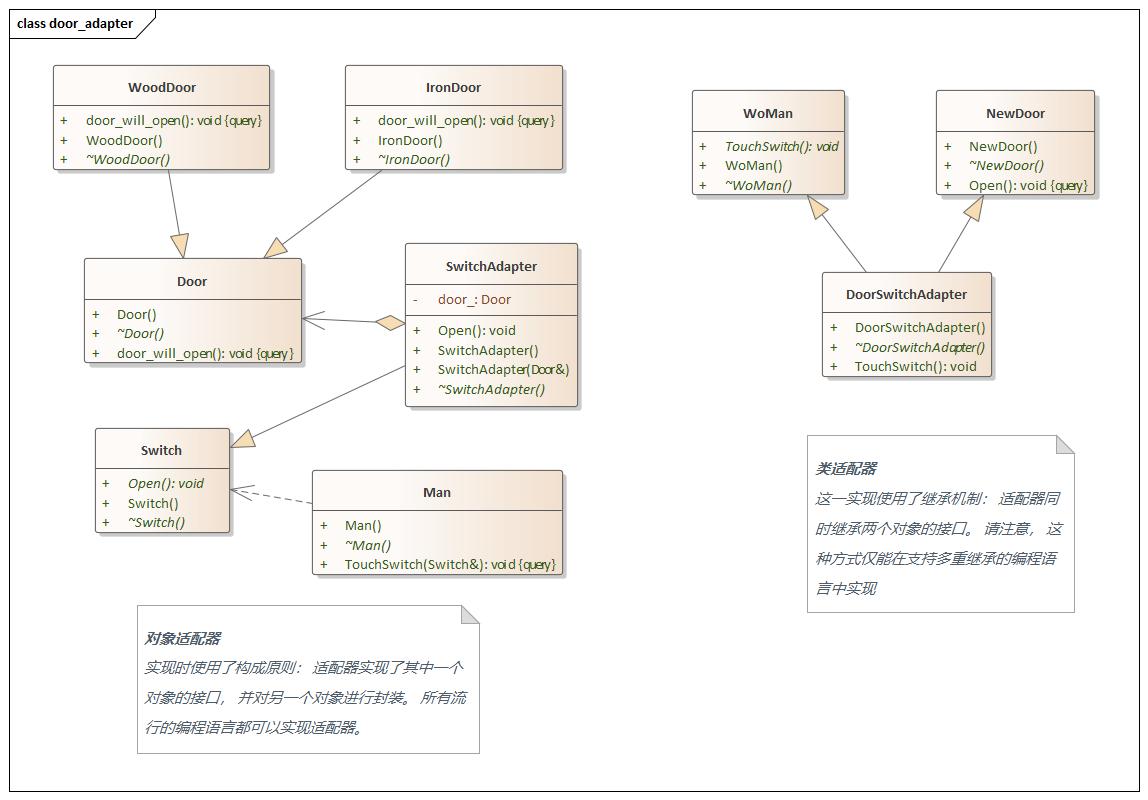
Adapter(适配器) 设计思想
Code
adapter.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 #ifndef PROTOTYPE_H #define PROTOTYPE_H namespace door_adapter {class Switch { public : Switch () = default ; virtual ~Switch () = default ; virtual void Open () 0 ; }; class Man { public : Man () = default ; virtual ~Man () = default ; void TouchSwitch (Switch & switch_) const switch_.Open (); } }; class Door { public : Door () = default ; virtual ~Door () = default ; void door_will_open () const std::cout << "Door is opening." << std::endl; } }; class WoodDoor :public Door{ using Door::Door; public : WoodDoor () = default ; virtual ~WoodDoor () = default ; void door_will_open () const std::cout << "Wood Door is opening." << std::endl; } }; class IronDoor :public Door{ using Door::Door; public : IronDoor () = default ; virtual ~IronDoor () = default ; void door_will_open () const std::cout << "Iron Door is opening." << std::endl; } }; class SwitchAdapter :public Switch{ public : SwitchAdapter () = default ; SwitchAdapter (Door &door) : door_ (door) {} virtual ~SwitchAdapter () = default ; void Open () override door_.door_will_open (); } private : Door door_; }; class WoMan { public : WoMan () = default ; virtual ~WoMan () = default ; virtual void TouchSwitch () 0 ; }; class NewDoor { public : NewDoor () = default ; virtual ~NewDoor () = default ; void Open () const std::cout << "New Door is opening" << std::endl; } }; class DoorSwitchAdapter :public WoMan, private NewDoor{ public : DoorSwitchAdapter () = default ; virtual ~DoorSwitchAdapter () = default ; void TouchSwitch () this ->Open (); } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <iostream> #include "adapter.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace door_adapter;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) #if 0 Door door; SwitchAdapter door_switch (door) ; Man man; man.TouchSwitch (door_switch); #endif DoorSwitchAdapter door_switch_adapter_; door_switch_adapter_.TouchSwitch (); return 0 ; }
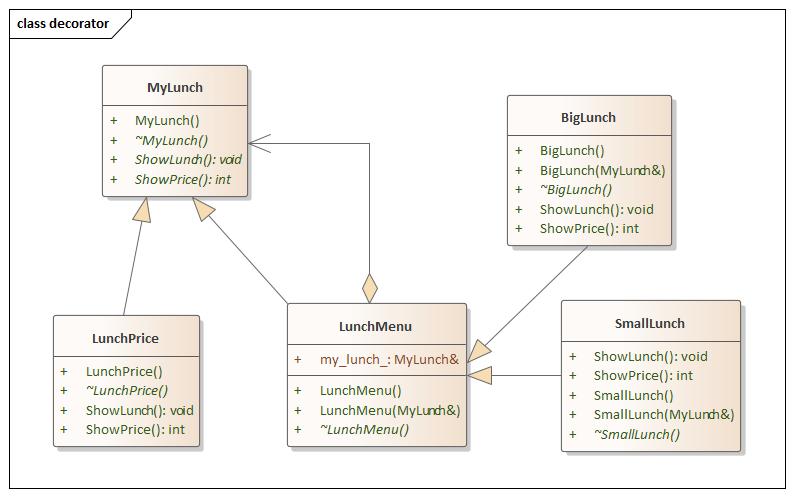
Decorator(装饰) 设计思想
Code
decorator.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #ifndef DECORATIOR_HPP #define DECORATIOR_HPP #include <iostream> using namespace std;namespace decorator {class MyLunch {public : MyLunch () = default ; virtual ~MyLunch () = default ; virtual void ShowLunch () 0 ; virtual int ShowPrice () 0 ; }; class LunchPrice :public MyLunch {public : LunchPrice () = default ; virtual ~LunchPrice () = default ; void ShowLunch () override } int ShowPrice () override return 5 ; } }; class LunchMenu :public MyLunch {public : LunchMenu () = default ; LunchMenu (MyLunch& my_lunch) : my_lunch_ (my_lunch) {} virtual ~LunchMenu () = default ; MyLunch& my_lunch_; }; class SmallLunch :public LunchMenu {public : SmallLunch () = default ; SmallLunch (MyLunch& my_lunch) : LunchMenu (my_lunch) {} virtual ~SmallLunch () = default ; int ShowPrice () override return my_lunch_.ShowPrice () + 10 ; } void ShowLunch () override std::cout << "Rich + Avergage" << std::endl; } }; class BigLunch :public LunchMenu {public : BigLunch () = default ; BigLunch (MyLunch& my_lunch) : LunchMenu (my_lunch) {} virtual ~BigLunch () = default ; int ShowPrice () override return my_lunch_.ShowPrice () + 20 ; } void ShowLunch () override std::cout << "Rich + Avergage + Milk" << std::endl; } }; } #endif
decorator.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "decorator.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace decorator;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) LunchPrice lunch_price; SmallLunch small_lunch (lunch_price) ; BigLunch big_lunch (lunch_price) ; small_lunch.ShowLunch (); std::cout << small_lunch.ShowPrice () << std::endl; big_lunch.ShowLunch (); std::cout << big_lunch.ShowPrice () << std::endl; return 0 ; }
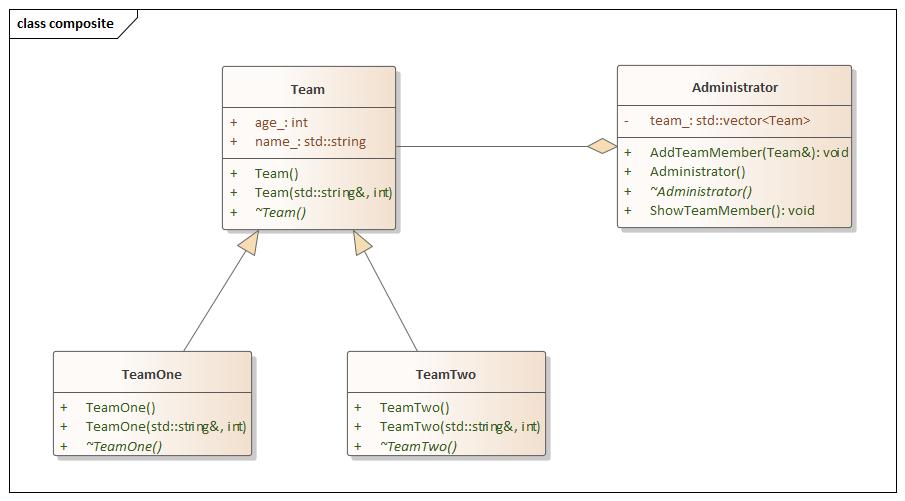
Composite(组合) 设计思想
Code
composite.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 #ifndef COMPOSITE_HPP #define COMPOSITE_HPP #include <iostream> #include <vector> namespace composite {class Team {public : Team () = default ; Team (const std::string& name, int age) : name_ (name), age_ (age) {} virtual ~Team () = default ; std::string name_; int age_; }; class TeamOne :public Team {public : TeamOne () = default ; TeamOne (const std::string& name, int age) : Team (name, age) {} virtual ~TeamOne () = default ; }; class TeamTwo :public Team {public : TeamTwo () = default ; TeamTwo (const std::string& name, int age) : Team (name, age) {} virtual ~TeamTwo () = default ; }; class Administrator {public : Administrator () = default ; virtual ~Administrator () = default ; void AddTeamMember (Team& team) team_.push_back (team); } void ShowTeamMember () for (auto iter = team_.begin (); iter != team_.end (); ++iter) { std::cout << "Team Member Name: " << iter->name_ << std::endl; std::cout << "Team Member Age: " << iter->age_ << std::endl; } } private : std::vector<Team> team_; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "composite.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace composite;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) TeamOne team_one ("xiao hong" , 42 ) ; TeamTwo team_two ("xiao ming" , 43 ) ; Administrator administers; administers.AddTeamMember (team_one); administers.AddTeamMember (team_two); administers.ShowTeamMember (); return 0 ; }
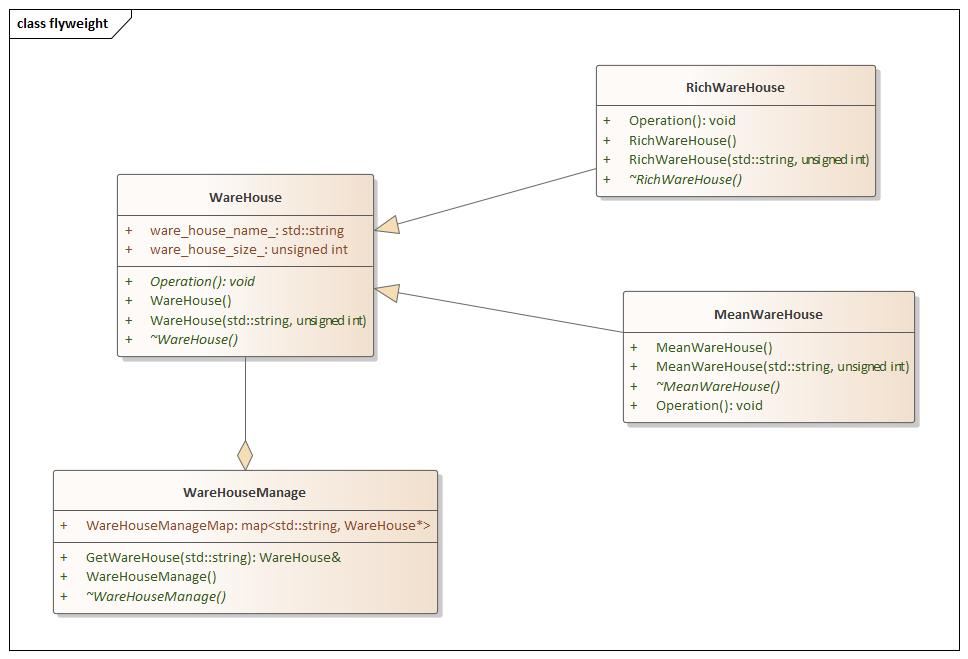
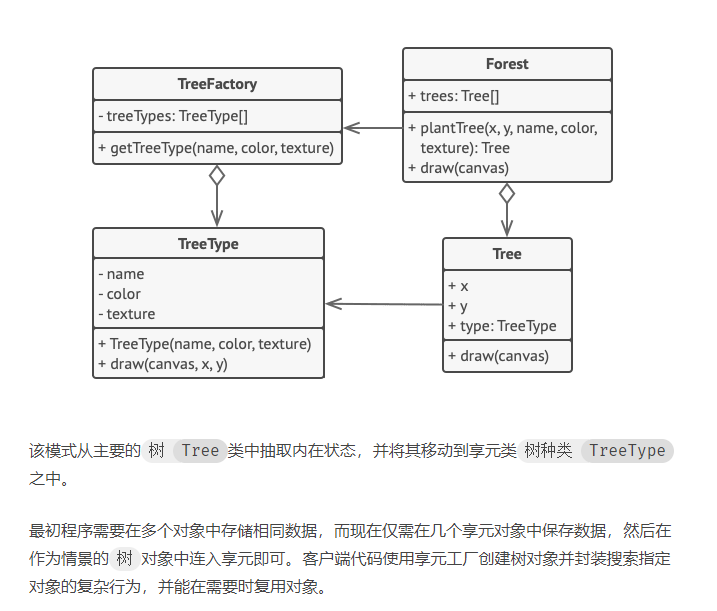
Flyweight(享元) 设计思想
Code
flyweight.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 #ifndef FLYWEIGHT_HPP #define FLYWEIGHT_HPP #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;namespace flyweight {class WareHouse {public : WareHouse () = default ; WareHouse (std::string name, unsigned int size = 36 ) : ware_house_name_ (name), ware_house_size_ (size) {} virtual ~WareHouse () = default ; virtual void Operation () 0 ; unsigned int ware_house_size_; std::string ware_house_name_; }; class MeanWareHouse :public WareHouse {public : MeanWareHouse () = default ; MeanWareHouse (std::string name, unsigned int size = 64 ) : WareHouse (name, size) {} virtual ~MeanWareHouse () = default ; void Operation () override std::cout << "Name: " << ware_house_name_ << std::endl; std::cout << "Size: " << ware_house_size_ << std::endl; } }; class RichWareHouse :public WareHouse {public : RichWareHouse () = default ; RichWareHouse (std::string name, unsigned int size = 64 ) : WareHouse (name, size) {} virtual ~RichWareHouse () = default ; void Operation () override std::cout << "Name: " << ware_house_name_ << std::endl; std::cout << "Size: " << ware_house_size_ << std::endl; } }; class WareHouseManage {public : WareHouseManage () = default ; virtual ~WareHouseManage () = default ; WareHouse& GetWareHouse (std::string ware_house_name) { if (WareHouseManageMap.find (ware_house_name) == WareHouseManageMap.end ()) { if (ware_house_name == "mean" ) { WareHouseManageMap[ware_house_name] = new MeanWareHouse (ware_house_name); } else if (ware_house_name == "rich" ) { WareHouseManageMap[ware_house_name] = new RichWareHouse (ware_house_name); } } return *(WareHouseManageMap[ware_house_name]); }; map<std::string, WareHouse*> WareHouseManageMap; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "flyweight.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace flyweight;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) WareHouseManage ware_house_manage; ware_house_manage.GetWareHouse ("mean" ).Operation (); ware_house_manage.GetWareHouse ("rich" ).Operation (); ware_house_manage.GetWareHouse ("mean" ).Operation (); ware_house_manage.GetWareHouse ("rich" ).Operation (); return 0 ; }
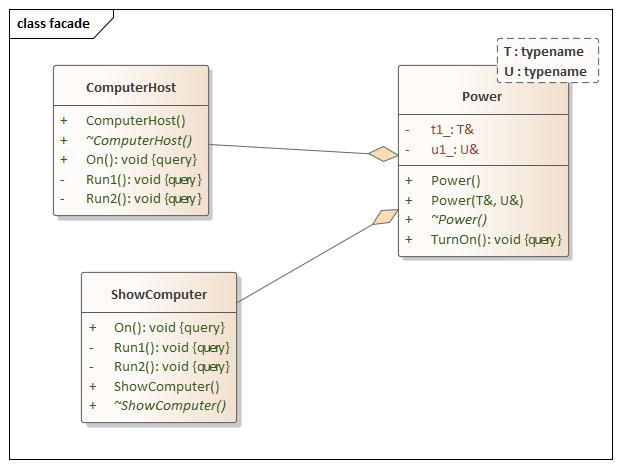
Facade(外观) 设计思想
Code
facade.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #ifndef FACADE_HPP #define FACADE_HPP #include <iostream> using namespace std;namespace facade {class ComputerHost {public : ComputerHost () = default ; virtual ~ComputerHost () = default ; void On () const Run1 (); Run2 (); } private : void Run1 () const std::cout << "ComputerHost Run1" << std::endl; } void Run2 () const std::cout << "ComputerHost Run2" << std::endl; } }; class ShowComputer {public : ShowComputer () = default ; virtual ~ShowComputer () = default ; void On () const Run1 (); Run2 (); } private : void Run1 () const std::cout << "ShowComputer Run1" << std::endl; } void Run2 () const std::cout << "ShowComputer Run2" << std::endl; } }; template <typename T, typename U>class Power {public : Power (); Power (T& t1, U& u1) : t1_ (t1), u1_ (u1) {} virtual ~Power () = default ; void TurnOn () const t1_.On (); u1_.On (); } private : T& t1_; U& u1_; }; template class Power <} #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <iostream> #include "facade.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace facade;extern template class Power <int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) ComputerHost computer_host; ShowComputer show_computer; Power<ComputerHost, ShowComputer> power (computer_host, show_computer) ; power.TurnOn (); return 0 ; }
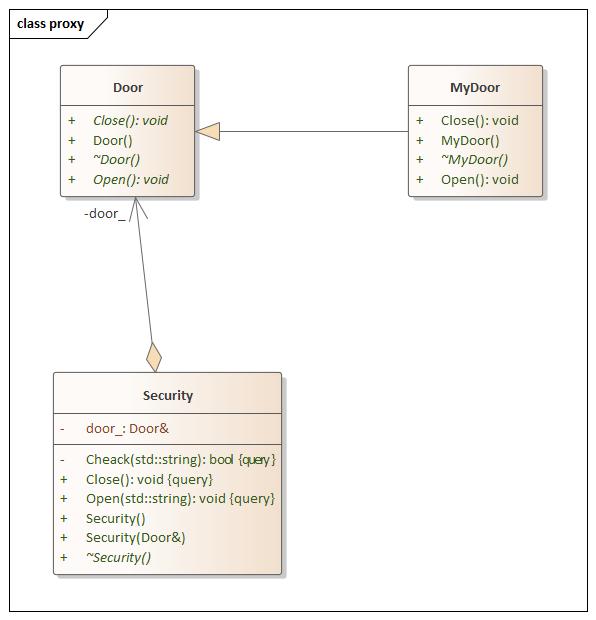
Proxy(代理) 设计思想
Code
proxy.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <iostream> using namespace std;namespace proxy {class Door {public : Door () = default ; virtual ~Door () = default ; virtual void Open () 0 ; virtual void Close () 0 ; }; class MyDoor :public Door{public : MyDoor () = default ; virtual ~MyDoor () = default ; void Open () override std::cout << "Open My Door" << std::endl; } void Close () override std::cout << "Close My Door" << std::endl; } }; class Security {public : Security () = default ; Security (Door& door) : door_ (door) {} virtual ~Security () = default ; void Open (const std::string passworld) const if (Cheack (passworld)) { door_.Open (); } else { std::cout << "Passworld is not right" << std::endl; } } void Close () const door_.Close (); } private : bool Cheack (std::string passworld) const passworld == "123" ? true : false ; } Door& door_; }; }
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <iostream> #include "proxy.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace proxy;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) MyDoor my_door; Security security (my_door) ; security.Open ("123" ); security.Open ("1" ); security.Close (); return 0 ; }
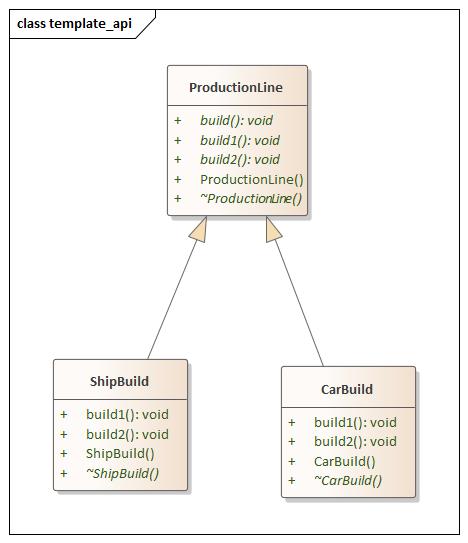
行为型 Template(模板) 设计思想
Code
template.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #ifndef TEMPLATE_HPP #define TEMPLATE_HPP #include <iostream> namespace template_api {class ProductionLine {public : ProductionLine () = default ; virtual ~ProductionLine () = default ; virtual void build () build1 (); build1 (); } virtual void build1 () 0 ; virtual void build2 () 0 ; }; class CarBuild :public ProductionLine {public : CarBuild () = default ; virtual ~CarBuild () = default ; void build1 () override std::cout << "Build Car Stop 1" << std::endl; } void build2 () override std::cout << "Build Cat Stop 2" << std::endl; } }; class ShipBuild :public ProductionLine {public : ShipBuild () = default ; virtual ~ShipBuild () = default ; void build1 () override std::cout << "Build Ship Stop 1" << std::endl; } void build2 () override std::cout << "Build Ship Stop 2" << std::endl; } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> #include "template.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace template_api;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) CarBuild car_build; ShipBuild ship_build; car_build.build (); ship_build.build (); return 0 ; }
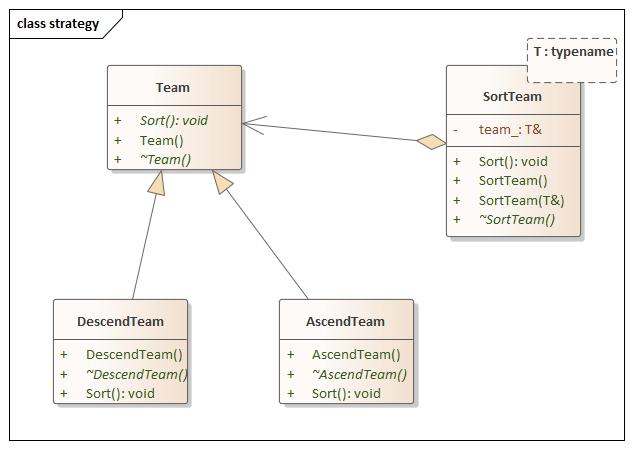
Strategy(策略) 设计思想
Code
strategy.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #ifndef STRATEGY_HPP #define STRATEGY_HPP #include <iostream> namespace strategy {class Team {public : Team () = default ; virtual ~Team () = default ; virtual void Sort () 0 ; }; class AscendTeam :public Team {public : AscendTeam () = default ; virtual ~AscendTeam () = default ; void Sort () override std::cout << "Sort By Ascend" << std::endl; } }; class DescendTeam :public Team {public : DescendTeam () = default ; virtual ~DescendTeam () = default ; void Sort () override std::cout << "Sort By Descend" << std::endl; } }; template <typename T>class SortTeam {public : SortTeam () = default ; SortTeam (T& team) : team_ (team) {} virtual ~SortTeam () = default ; void Sort () team_.Sort (); } private : T& team_; }; template class SortTeam <template class SortTeam <} #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "strategy.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace strategy;extern template class SortTeam <extern template class SortTeam <int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) SortTeam<AscendTeam> ascend_team (*(new AscendTeam)) ; SortTeam<DescendTeam> descend_team (*(new DescendTeam)) ; ascend_team.Sort (); descend_team.Sort (); return 0 ; }
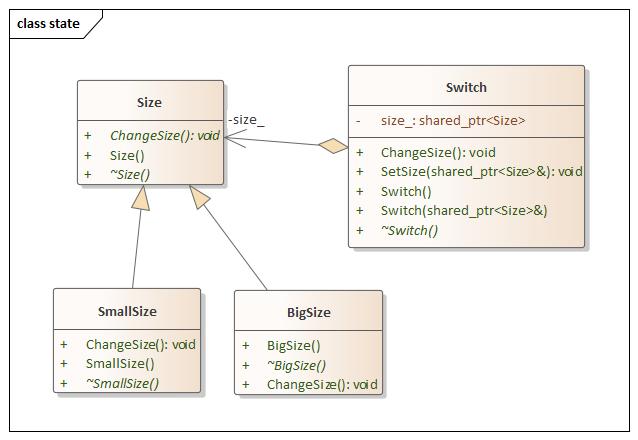
State(状态) 设计思想
Code
state.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #ifndef STATE_HPP #define STATE_HPP #include <iostream> #include <memory> using namespace std;namespace state {class Size {public : Size () = default ; virtual ~Size () = default ; virtual void ChangeSize () 0 ; }; class BigSize :public Size {public : BigSize () = default ; virtual ~BigSize () = default ; void ChangeSize () override std::cout << "Big Size" << std::endl; } }; class SmallSize :public Size {public : SmallSize () = default ; virtual ~SmallSize () = default ; void ChangeSize () override std::cout << "Small Size" << std::endl; } }; class Switch {public : Switch () = default ; explicit Switch (const shared_ptr<Size>& size) : size_(size) { } virtual ~Switch () = default ; void SetSize (const shared_ptr<Size>& size) size_ = size; } void ChangeSize () size_->ChangeSize (); } private : shared_ptr<Size> size_; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <iostream> #include "state.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace state;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Switch my_switch (make_shared<BigSize>()) ; my_switch.ChangeSize (); my_switch.SetSize (make_shared<SmallSize>()); my_switch.ChangeSize (); return 0 ; }
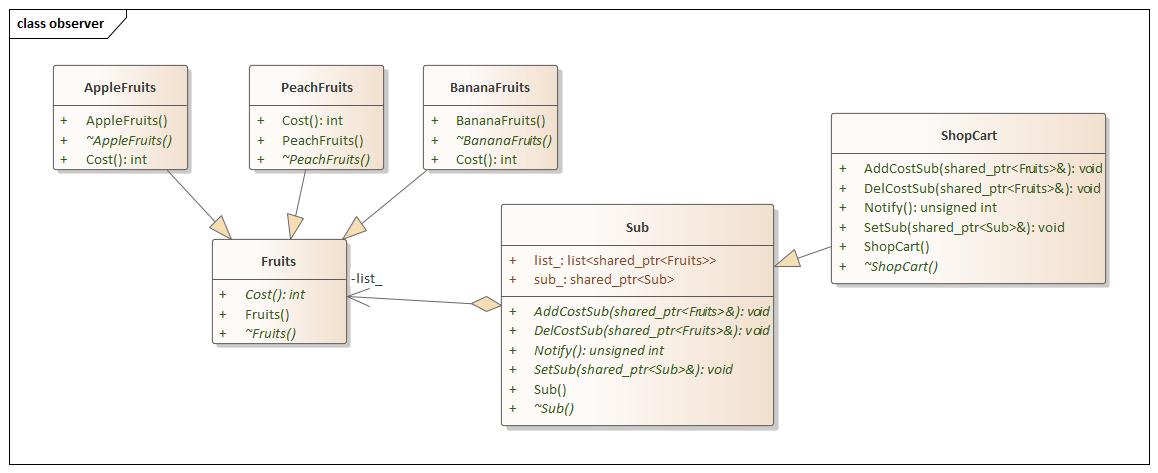
Observer(观察者) 设计思想
Code
observer.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #ifndef OBSERVER_HPP #define OBSERVER_HPP #include <iostream> #include <list> #include <memory> using namespace std;namespace observer {class Fruits {public : Fruits () = default ; virtual ~Fruits () = default ; virtual int Cost () 0 ; }; class AppleFruits :public Fruits {public : AppleFruits () = default ; virtual ~AppleFruits () = default ; int Cost () override return 5 ; } }; class BananaFruits :public Fruits {public : BananaFruits () = default ; virtual ~BananaFruits () = default ; int Cost () override return 11 ; } }; class PeachFruits :public Fruits {public : PeachFruits () = default ; virtual ~PeachFruits () = default ; int Cost () override return 3 ; } }; class Sub {public : Sub () = default ; virtual ~Sub () = default ; virtual void AddCostSub (const shared_ptr<Fruits>&) 0 ; virtual void DelCostSub (const shared_ptr<Fruits>&) 0 ; virtual unsigned int Notify () 0 ; virtual void SetSub (const shared_ptr<Sub>&) 0 ; list<shared_ptr<Fruits>> list_; shared_ptr<Sub> sub_; }; class ShopCart :public Sub {public : ShopCart () = default ; virtual ~ShopCart () = default ; void AddCostSub (const shared_ptr<Fruits>& fruits_sub) override list_.push_back (fruits_sub); } void DelCostSub (const shared_ptr<Fruits>& fruits_sub) override list_.remove (fruits_sub); } unsigned int Notify () override unsigned int num = 0 ; for (auto iter = list_.begin (); iter != list_.end (); ++iter) { num += (*iter)->Cost (); } return num; } void SetSub (const shared_ptr<Sub>& sub) override sub_ = sub; } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <iostream> #include "observer.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace observer;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) ShopCart shop_cart; shared_ptr<AppleFruits> apple_fruits = make_shared<AppleFruits>(); shared_ptr<BananaFruits> banana_fruits = make_shared<BananaFruits>(); shared_ptr<PeachFruits> peach_fruits = make_shared<PeachFruits>(); shop_cart.AddCostSub (apple_fruits); std::cout << shop_cart.Notify () << std::endl; shop_cart.AddCostSub (banana_fruits); std::cout << shop_cart.Notify () << std::endl; shop_cart.AddCostSub (peach_fruits); std::cout << shop_cart.Notify () << std::endl; shop_cart.DelCostSub (apple_fruits); shop_cart.DelCostSub (banana_fruits); shop_cart.DelCostSub (peach_fruits); return 0 ; }
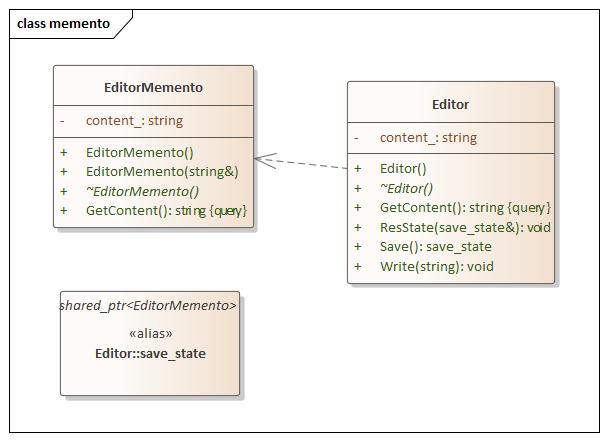
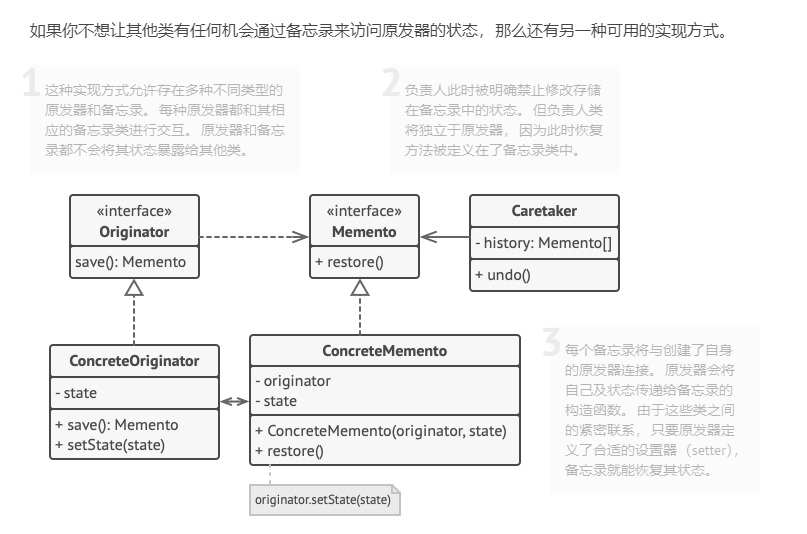
Memento(备忘录) 设计思想
Code
memento.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #ifndef MEMENTO_HPP #define MEMENTO_HPP #include <iostream> #include <memory> using namespace std;namespace memento {class EditorMemento {public : EditorMemento () = delete ; explicit EditorMemento (const string& content) : content_(content) { } string GetContent () const {return content_;} virtual ~EditorMemento () = default ; private : string content_; }; class Editor { using save_state = shared_ptr<EditorMemento>; public : Editor () = default ; virtual ~Editor () = default ; void Write (string content) content_ = content; } save_state Save () { return make_shared<EditorMemento>(content_); } void ResState (save_state& save) content_ = save->GetContent (); } string GetContent () const {return content_;} private : string content_; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <iostream> #include "memento.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace memento;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Editor editor_; editor_.Write ("Hello World" ); std::cout << "1321" << std::endl; std::cout << editor_.GetContent () << std::endl; auto save = editor_.Save (); editor_.Write ("Bye Bye" ); std::cout << editor_.GetContent () << std::endl; editor_.ResState (save); std::cout << editor_.GetContent () << std::endl; return 0 ; }
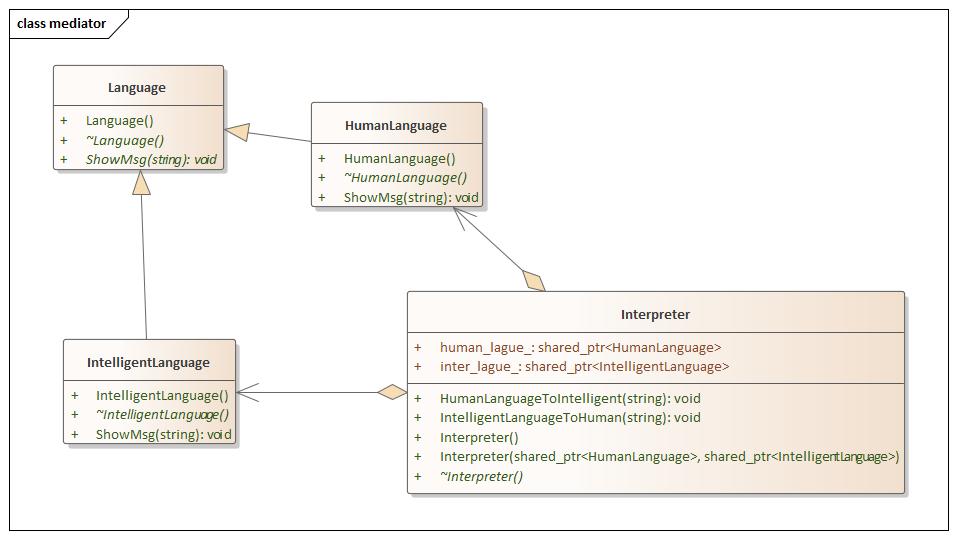
设计思想
Code
mediator.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #ifndef MEDIATOR_HPP #define MEDIATOR_HPP #include <iostream> #include <memory> using namespace std;namespace mediator {class Interpreter ;class Language {public : Language () = default ; virtual ~Language () = default ; virtual void ShowMsg (string msg) 0 ; }; class HumanLanguage :public Language {public : HumanLanguage () = default ; virtual ~HumanLanguage () = default ; void ShowMsg (string msg) override std::cout << "This is Human Language: " << msg << std::endl; } }; class IntelligentLanguage :public Language {public : IntelligentLanguage () = default ; virtual ~IntelligentLanguage () = default ; void ShowMsg (string msg) override std::cout << "This is Intelligent Language: " << msg << std::endl; } }; class Interpreter {public : Interpreter () = delete ; Interpreter (shared_ptr<HumanLanguage> human_lague, shared_ptr<IntelligentLanguage> inter_lague) : human_lague_ (human_lague), inter_lague_ (inter_lague) {} virtual ~Interpreter () = default ; shared_ptr<HumanLanguage> human_lague_; shared_ptr<IntelligentLanguage> inter_lague_; void HumanLanguageToIntelligent (string msg) inter_lague_->ShowMsg (msg); } void IntelligentLanguageToHuman (string msg) human_lague_->ShowMsg (msg); } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <iostream> #include "mediator.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace mediator;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) shared_ptr<HumanLanguage> human = make_shared<HumanLanguage>(); shared_ptr<IntelligentLanguage> intel = make_shared<IntelligentLanguage>(); Interpreter inter (human, intel) ; inter.HumanLanguageToIntelligent ("Hello World" ); inter.IntelligentLanguageToHuman ("Bye Bye" ); return 0 ; }
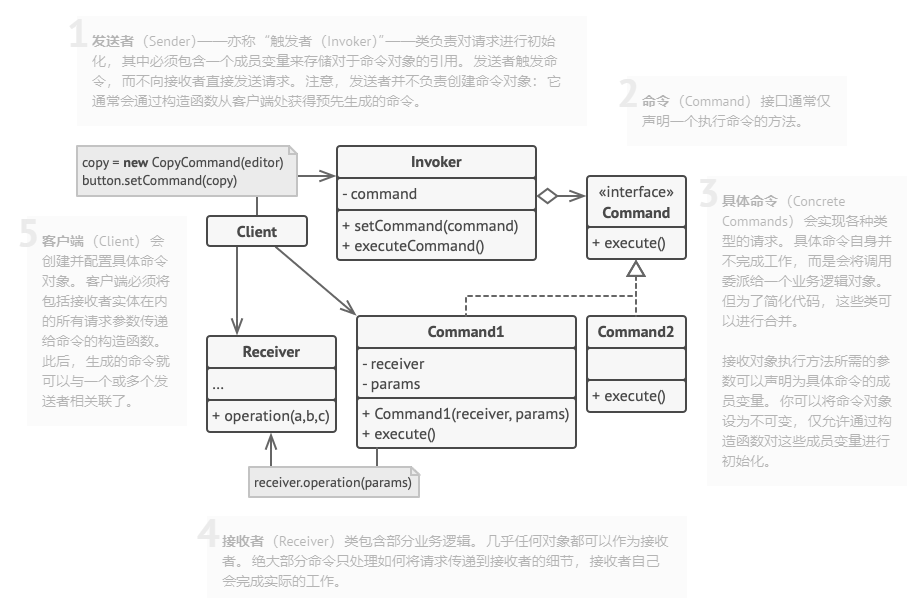
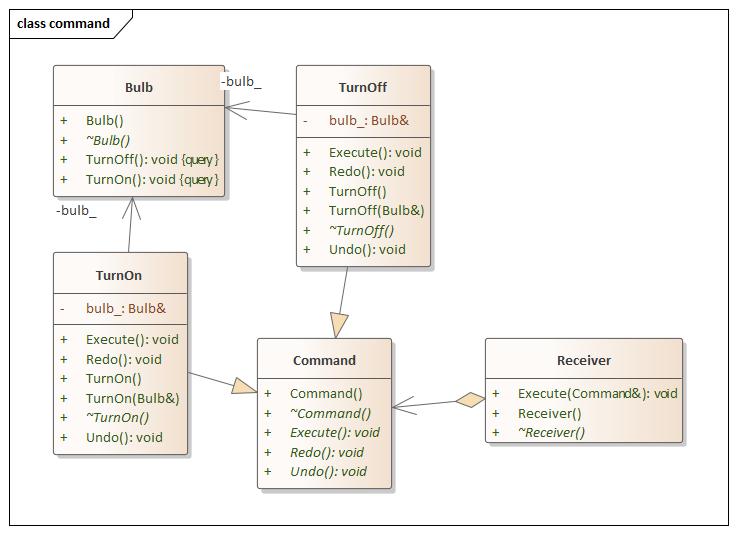
Command(命令) 设计思想
Code
command.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 #ifndef COMMAND_HPP #define COMMAND_HPP #include <iostream> using namespace std;namespace command {class Bulb {public : Bulb () = default ; virtual ~Bulb () = default ; void TurnOn () const std::cout << "The Bulb Turn On" << std::endl; } void TurnOff () const std::cout << "The Bulb Turn Off" << std::endl; } }; class Command {public : Command () = default ; virtual ~Command () = default ; virtual void Execute () 0 ; virtual void Undo () 0 ; virtual void Redo () 0 ; }; class TurnOn :public Command {public : TurnOn () = default ; explicit TurnOn (Bulb& bulb) : bulb_(bulb) { } virtual ~TurnOn () = default ; void Execute () override bulb_.TurnOff (); } void Undo () override bulb_.TurnOn (); } void Redo () override Execute (); } private : Bulb& bulb_; }; class TurnOff :public Command {public : TurnOff () = default ; TurnOff (Bulb& bulb) : bulb_ (bulb) {} virtual ~TurnOff () = default ; void Execute () override bulb_.TurnOff (); } void Undo () override bulb_.TurnOn (); } void Redo () override Execute (); } private : Bulb& bulb_; }; class Receiver {public : Receiver () = default ; virtual ~Receiver () = default ; void Execute (Command& cmd) cmd.Execute (); } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <iostream> #include "command.hpp" using namespace command;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Bulb bulb; TurnOff turn_off (bulb) ; TurnOn turn_on (bulb) ; Receiver recv; recv.Execute (turn_on); recv.Execute (turn_off); return 0 ; }
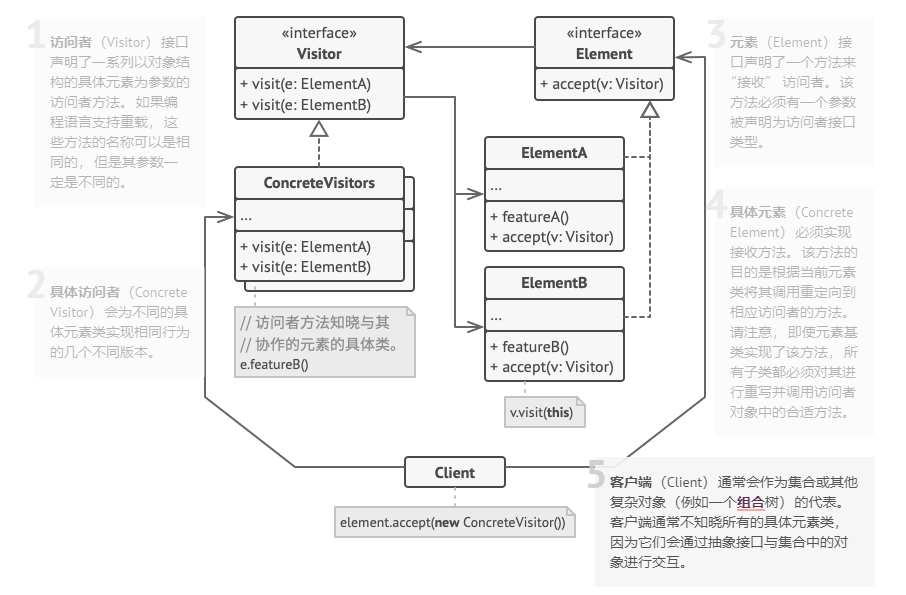
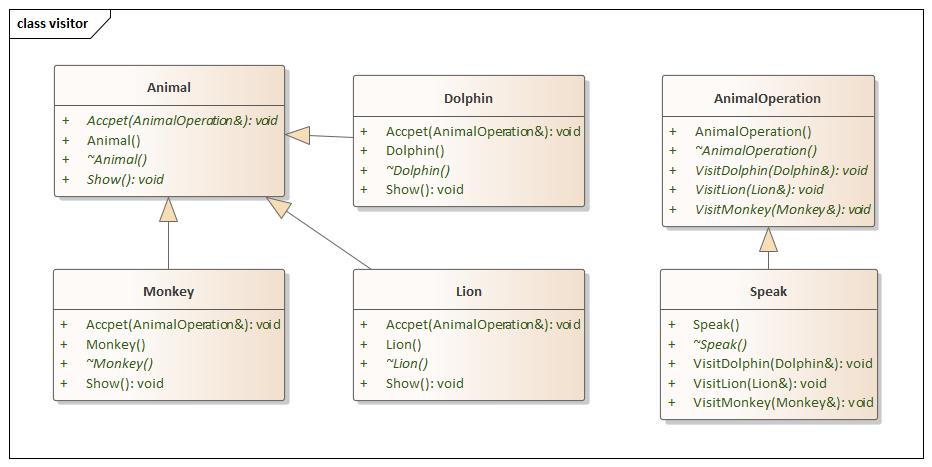
Visitor(访问者) 设计思想
Code
command.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 #ifndef COMMAND_HPP #define COMMAND_HPP #include <iostream> using namespace std;namespace command {class Bulb {public : Bulb () = default ; virtual ~Bulb () = default ; void TurnOn () const std::cout << "The Bulb Turn On" << std::endl; } void TurnOff () const std::cout << "The Bulb Turn Off" << std::endl; } }; class Command {public : Command () = default ; virtual ~Command () = default ; virtual void Execute () 0 ; virtual void Undo () 0 ; virtual void Redo () 0 ; }; class TurnOn :public Command {public : TurnOn () = default ; explicit TurnOn (Bulb& bulb) : bulb_(bulb) { } virtual ~TurnOn () = default ; void Execute () override bulb_.TurnOff (); } void Undo () override bulb_.TurnOn (); } void Redo () override Execute (); } private : Bulb& bulb_; }; class TurnOff :public Command {public : TurnOff () = default ; TurnOff (Bulb& bulb) : bulb_ (bulb) {} virtual ~TurnOff () = default ; void Execute () override bulb_.TurnOff (); } void Undo () override bulb_.TurnOn (); } void Redo () override Execute (); } private : Bulb& bulb_; }; class Receiver {public : Receiver () = default ; virtual ~Receiver () = default ; void Execute (Command& cmd) cmd.Execute (); } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <iostream> #include "command.hpp" using namespace command;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Bulb bulb; TurnOff turn_off (bulb) ; TurnOn turn_on (bulb) ; Receiver recv; recv.Execute (turn_on); recv.Execute (turn_off); return 0 ; }
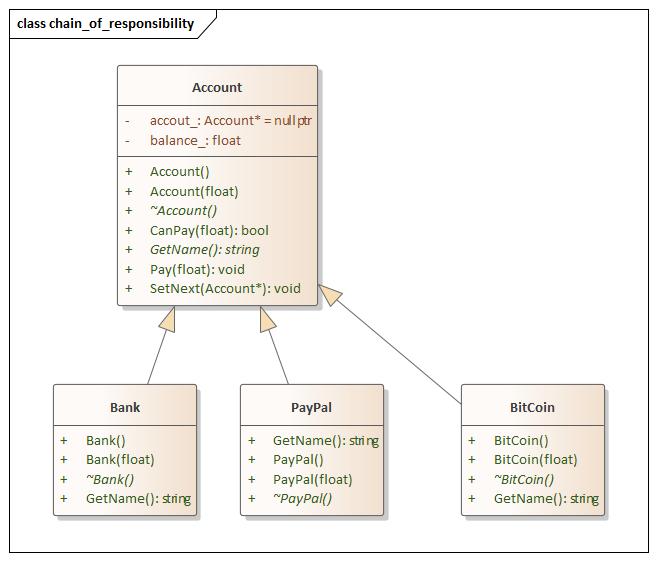
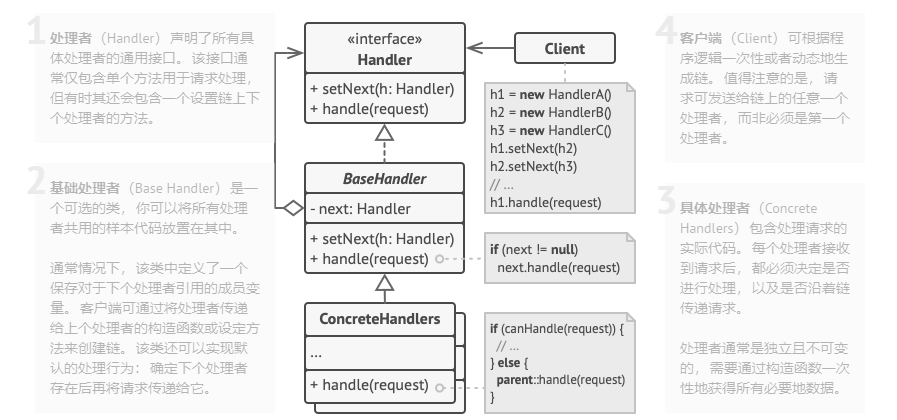
Chain of Responsibility(责任链模式) 设计思想
Code
chain_of_responsibility.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 #ifndef CHAIN_OF_RESPONSIBILITY_HPP #define CHAIN_OF_RESPONSIBILITY_HPP #include <iostream> #include <memory> using namespace std;namespace chain_of_responsibility {class Account {public : Account () = default ; Account (float balance) : balance_ (balance) {} virtual ~Account () = default ; virtual string GetName () 0 ; void SetNext (Account* accout) accout_ = accout; } bool CanPay (float amount_to_pay) return amount_to_pay <= balance_ ? true : false ; } void Pay (float amount_to_pay) if (CanPay (amount_to_pay)) { std::cout << this ->GetName () << "Can Pay" << std::endl; } else if (accout_ != nullptr ) { accout_->Pay (amount_to_pay); } else { std::cout << this ->GetName () << "Failed" << std::endl; } } private : Account* accout_ = nullptr ; float balance_; }; class Bank :public Account {public : Bank () = default ; Bank (float balance) : Account (balance) {} virtual ~Bank () = default ; string GetName () { return "Bank" ; } }; class PayPal :public Account {public : PayPal () = default ; PayPal (float balance) : Account (balance) {} virtual ~PayPal () = default ; string GetName () { return "PayPal" ; } }; class BitCoin :public Account {public : BitCoin () = default ; BitCoin (float balance) : Account (balance) {} virtual ~BitCoin () = default ; string GetName () { return "BitCoin" ; } }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> #include "chain_of_responsibility.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace chain_of_responsibility;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Bank bank (100 ) ; PayPal pay_pal (200 ) ; BitCoin bit_coin (300 ) ; bank.SetNext (&pay_pal); pay_pal.SetNext (&bit_coin); bank.Pay (223 ); return 0 ; }
Iterator(迭代器) 设计思想
Code
Iterator.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #ifndef ITERATOR_HPP #define ITERATOR_HPP #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;namespace iterator_api {class RadioStation {public : RadioStation () = default ; RadioStation (float frequency) : frequency_ (frequency) {} virtual ~RadioStation () = default ; float GetFrequency () const return frequency_; } friend bool operator ==(const RadioStation& lhs, const RadioStation& rhs) { }; private : float frequency_; }; class StationList { using iter = std::vector<RadioStation>::iterator; public : StationList () = default ; virtual ~StationList () = default ; void AddStation (const RadioStation& station) station_.push_back (station); }; void RemoveStation (const RadioStation& to_remove) auto found = std::find (station_.begin (), station_.end (), to_remove); if (found != station_.end ()) { station_.erase (found); } } iter begin () { return station_.begin (); } iter end () { return station_.end (); } private : std::vector<RadioStation> station_; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <iostream> #include "Iterator.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace iterator_api;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) StationList station_list; station_list.AddStation (RadioStation (89 )); station_list.AddStation (RadioStation (101 )); station_list.AddStation (RadioStation (102 )); station_list.AddStation (RadioStation (103.2 )); for (auto && station : station_list) { std::cout << station.GetFrequency () << std::endl; } station_list.RemoveStation (RadioStation (89 )); for (auto && station : station_list) { std::cout << station.GetFrequency () << std::endl; } return 0 ; }
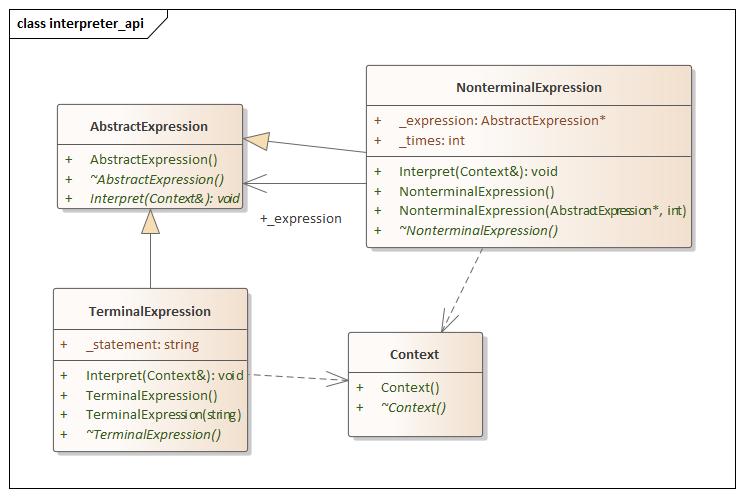
Interpreter(解释器) 设计思想
Code
interpreter.hpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #ifndef INTERPTRTER_HPP #define INTERPTRTER_HPP #include <iostream> using namespace std;namespace interpreter_api {class Context { public : Context () = default ; virtual ~Context () = default ; }; class AbstractExpression { public : AbstractExpression () = default ; virtual ~AbstractExpression () = default ; virtual void Interpret (Context& c) 0 ; }; class TerminalExpression :public AbstractExpression{ public : TerminalExpression () = default ; TerminalExpression (string statement) { _statement = statement; } virtual ~TerminalExpression () = default ; void Interpret (Context& c) std::cout << this ->_statement << "TerminalExpression" << std::endl; } string _statement; }; class NonterminalExpression :public AbstractExpression{ public : NonterminalExpression () = default ; NonterminalExpression (AbstractExpression* expression, int times) { this ->_expression = expression; this ->_times = times; } virtual ~NonterminalExpression () = default ; void Interpret (Context& c) override for (int i = 0 ; i < _times ; i++) { this ->_expression->Interpret (c); } } AbstractExpression* _expression; int _times; }; } #endif
main.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <iostream> #include "interpreter.hpp" using namespace std;using namespace interpreter_api;int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) Context* c = new Context (); string str = "hello" ; AbstractExpression* te = new TerminalExpression (str); AbstractExpression* nte = new NonterminalExpression (te, 2 ); nte->Interpret (*c); return 0 ; }